使用方法
export CC=afl-clang;export CXX=afl-clang++;
test.c为待测程序代码
afl-gcc -g -o afl_test afl_test.c
对那些可以直接从stdin读取输入的目标程序来说,语法如下:
./afl-fuzz -i testcase_dir -o findings_dir /path/to/program […params…]
对从文件读取输入的目标程序来说,要用“@@”,语法如下:
./afl-fuzz -i testcase_dir -o findings_dir /path/to/program @@
|
程序
一
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
void test (char *buf) {
int n = 0;
if(buf[0] == 'a') n++;
if(buf[1] == 'f') n++;
if(buf[2] == 'l') n++;
if(buf[3] == '!') n++;
if(n == 4) {
printf("awesome!\n");
raise(SIGSEGV);
}else{
printf("wrong!\n");
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
FILE* fp;
fp = fopen(argv[1],"r");
char buf[100];
fgets(buf,1024,fp);
test(buf);
return 0;
}
|
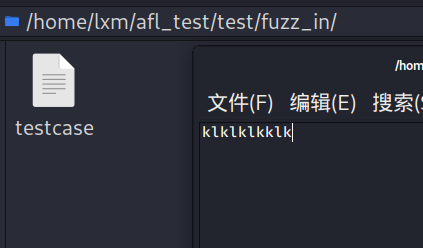
在输入文件夹(这里是fuzz_in)建立testcase文件,内容位任一可以使程序正常运行的输入
afl-gcc -g -o ./test ./test.c
afl-fuzz -i fuzz_in -o fuzz_out ./test @@
|
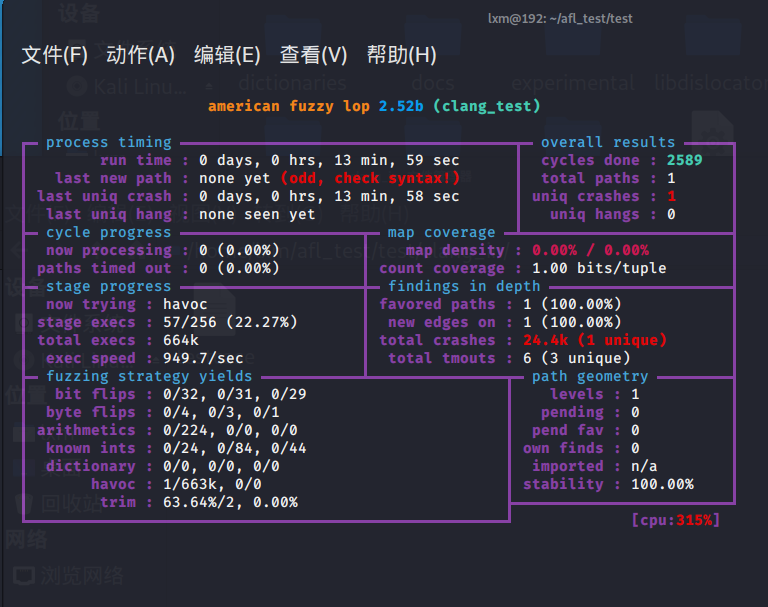
使用afl-clang:
分析出了1个uniq crashes

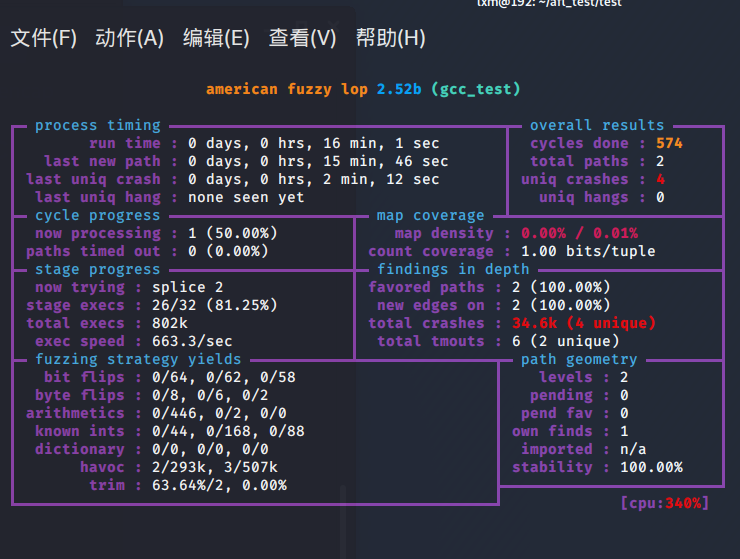
使用afl-gcc
分析出了4个uniq crashes

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void why_here(void)
{
printf("why r u here?\n");
exit(0);
}
void f()
{
char buff[2];
buff[2]=(int)why_here;
reutrn;
}
void main()
{
f();
return;
}
|